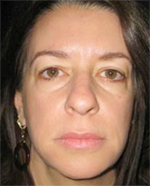
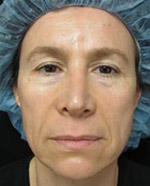
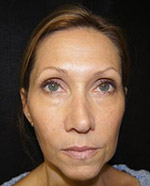
Signs of Aging
As our bodies age, the appearance and physical qualities of our skin change.
Over time, the skin loses its underlying layers of fat, and the production of collagen and elastin fibers slows. As a result, the skin loses its fullness and starts to sag.
Aging skin has the following qualities:
- It becomes thinner.
- It develops fine lines and wrinkles.
- It develops darkened spots called lentigines.
- It becomes drier and susceptible to itching.
- It loses underlying fat, leading to hollowed areas near the eyes and cheeks. This loss of fat also causes tendons and blood vessels in the hands to become more noticeable.
- Hair loses pigment and turns gray or white hairs.
This change is slow and continuous, starting in our twenties. The pace of aging is due to a combination of genes (our inherited tendency) and external factors, such as exposure to sunlight and its ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and smoking.
Just a few minutes of sun exposure each day can cause noticeable changes to the skin over time. The term “photoaging” is used to describe this sun-related skin damage. In sunny climates, photoaging may be seen in people as early as in their twenties.
To minimize the premature aging of the skin, practice sun protection habits. And, if you are a smoker, you may see improvement in your skin after quitting, even if you have smoked for many years.
Aging skin should be examined regularly for precancerous and cancerous lesions. Doing this at home is referred to as a skin self-exam.
Treatments for aging skin
If you are bothered by visible signs of aging, there are a variety of treatments available to improve damaged skin:
- Dermal fillers, or soft-tissue fillers, can be injected into the skin to fill out areas that look hollowed or wrinkled.
- Botox is a purified form of botulinum toxin that is injected into targeted facial muscles to prevent and correct wrinkles and other damage related to certain facial expressions (such as squinting or frowning).
- Dermabrasion is a common treatment in which the top layer of skin is abraded so that a new, smoother layer grows in its place. It’s used for many skin conditions, including acne, skin cancer, and photoaging.
- Chemical peels have many dermatological uses, including the treatment of wrinkles, age spots, and scars; a chemical solution is carefully applied to the skin to remove damaged outer layers, leaving smoother contours and an improved appearance.
- Laser resurfacing helps correct wrinkles and age spots through use of a laser that vaporizes damaged skin tissue.
- Unwanted hair can be removed through one or more methods, including waxing, chemical depilation, electrolysis, or laser removal; for best results, all methods should be performed or supervised by an experienced dermatologist.
- Liposuction is a way to reduce visible effects of aging by vaporizing and removing unwanted fat deposits that don’t respond to diet or exercise. Common target areas include the face, chin, neck, hips, and buttocks.
- Microdermabrasion gently scrapes away damaged and aging skin to trigger the growth of new layers.
- Topical medications, such as topical retinoids, have been shown to reduce fine wrinkles, splotchy darkened areas, and signs of chronic sun exposure.
- Over-the-counter products, such as moisturizers and “cosmeceuticals,” products containing agents designed to reduce the signs of aging, such as alpha-hydroxy acids or antioxidants.
These may be used alone or in combination for a more complete skin care regimen.
In helping you evaluate your treatment options, your physician will consider these factors:
- Areas to be treated
- Darkness of your skin
- Results of past treatments
- Personal preferences
Source: www.fromyourdoctor.com