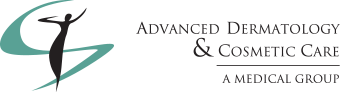The Mohs Procedure & Process
The Mohs surgery procedure is a simple concept: the surgeon removes the cancer, carefully checks to be sure the entire cancer is gone, and then repairs the wound. This page describes the steps they follow for each Mohs surgical procedure.
 Step 1
Step 1
The roots of a skin cancer may extend beyond the visible portion of the tumor. If these roots are not removed, the cancer will recur. A surgery starts with examining the visible lesion and planning what tissue to remove. The patient then receives local anesthesia, and the Mohs surgery begins.
 Step 2
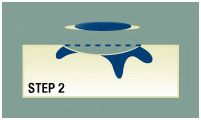
Step 2
The surgeon removes the visible portion of the tumor using careful surgical techniques. The removed skin is then processed into a slide. Next the surgeon assess the slide under a microsope to determine if there are any area still positive with cancer. If margins of the removed skin still shows residual skin cancer then another level of skin will be removed.
 Step 3
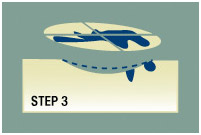
Step 3
The surgeon next removes a deeper layer of skin and divides it into sections. The surgeon color-codes each of these sections with dyes and makes reference marks on the skin to show the source of the sections. Next, a map of the surgical site is drawn to track exactly where each small portion of tissue originated.
 Step 4
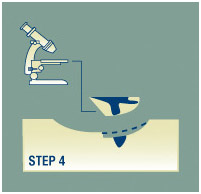
Step 4
The surgeon uses a microscope to examine the undersurface and edges of each section of tissue in search of evidence of remaining cancer.
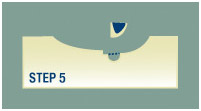 Step 5
Step 5
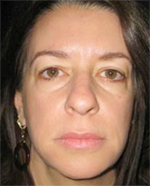
If the surgeon finds remaining cancer cells under the microscope the location of the remaining cancerous cells are marked on the surgical map. The surgeon then removes another deeper layer of skin, but only from precisely where the cancer cells originated. This results in the highest level cure rate and also leaves as much healthy tissue as possible. This contributes to the smallest scar possible as well.
Step 6
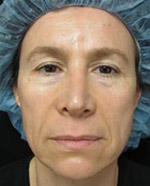
The removal process is complete when there is no longer any evidence of cancerous cells remaining and that all cancer roots have been removed. The next step is the reconstruction of the wound. The objective is to ensure the smallest scar or the most cosmetically friendly scar for the surgical wound.